Linux VSFTPD ile FTP Server Kurulumu
VSFTPD Nedir?
`vsftpd`, "Very Secure FTP Daemon"ın kısaltmasıdır ve Linux ve diğer Unix tabanlı işletim sistemlerinde kullanılan bir FTP sunucu yazılımıdır. FTP (File Transfer Protocol), dosyaların bir bilgisayardan diğerine iletilmesi için kullanılan bir ağ protokolüdür. vsftpd, bu protokolü kullanarak dosya transferi yapabilmenizi sağlar.
VSFTPD Özellikleri
- Güvenlik Odaklı: vsftpd, adından da anlaşılacağı gibi çok güvenli bir FTP sunucusudur. Güvenlikle ilgili birçok özelliğe sahiptir ve varsayılan olarak güvenlik önlemleri etkinleştirilmiştir.
- Performans: vsftpd, yüksek performanslı bir FTP sunucusudur. Hafif ve etkili bir tasarıma sahiptir, bu da hızlı ve verimli dosya transferleri sağlar.
- Pasif ve Aktif Mod Desteği: Hem pasif hem de aktif FTP modlarını destekler. Bu, farklı ağ konfigürasyonlarına uyum sağlar.
- Virtual Users ve Sanal Kullanıcı Desteği: vsftpd, sistemdeki gerçek kullanıcıların yanı sıra, sanal kullanıcılarla da çalışabilir. Bu, FTP kullanıcıları için özel bir yapılandırma sağlar.
- IPv6 Desteği: vsftpd, IPv6 ağlarını da destekler, bu da gelecekteki ağ altyapılarına uyumluluk sağlar.
- Yazma İzni Yönetimi: Kullanıcıların dosyalara yazma izni kontrolü, vsftpd'nin esnek yapılandırma seçenekleri ile yönetilebilir.
- Günlük ve Loglama Desteği: vsftpd, sistem olaylarını kaydetmek ve izlemek için günlük mekanizmalarını destekler.
vsftpd, genellikle sunucuların dosya transferi için kullanıldığı durumlarda tercih edilen bir FTP sunucusu seçeneğidir. Ancak, kullanırken güvenlik ayarlarını iyi bir şekilde yapılandırmak ve güncel tutmak önemlidir. Bu, potansiyel güvenlik açıklarını en aza indirir ve dosya transferleri sırasında bilgi güvenliğini sağlar.
VSFTPD Kurulumu
sudo apt update
sudo apt install vsftpd
sudo systemctl status vsftpd
vsftpd.service - vsftpd FTP serverLoaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-11-15 03:54:23 +03; 17min ago...
sudo nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
vsftpd.conf Dosyası
local_enable=YES # # Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command. write_enable=YES # # Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to 022, # if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's) #local_umask=022 # # Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This only # has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also, you will # obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user. #anon_upload_enable=YES # # Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create # new directories. #anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES # # Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they # go into a certain directory. dirmessage_enable=YES # # If enabled, vsftpd will display directory listings with the time # in your local time zone. The default is to display GMT. The # times returned by the MDTM FTP command are also affected by this # option. use_localtime=YES # # Activate logging of uploads/downloads. xferlog_enable=YES # # Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data). connect_from_port_20=YES # # If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned by # a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not # recommended! #chown_uploads=YES #chown_username=whoever # # You may override where the log file goes if you like. The default is shown # below. #xferlog_file=/var/log/vsftpd.log # # If you want, you can have your log file in standard ftpd xferlog format. # Note that the default log file location is /var/log/xferlog in this case. #xferlog_std_format=YES # # You may change the default value for timing out an idle session. #idle_session_timeout=600 # # You may change the default value for timing out a data connection. #data_connection_timeout=120 # # It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which the # ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user. #nopriv_user=ftpsecure # # Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests. Not # recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it, # however, may confuse older FTP clients. #async_abor_enable=YES # # By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact ignore # the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do ASCII # mangling on files when in ASCII mode. # Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of service # attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd # predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of the # raw file. # ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol. #ascii_upload_enable=YES #ascii_download_enable=YES # # You may fully customise the login banner string: ftpd_banner=Welcome to UbuntuServer Rasppberry Pi FTP service. # # You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses. Apparently # useful for combatting certain DoS attacks. #deny_email_enable=YES # (default follows) #banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd.banned_emails # # You may restrict local users to their home directories. See the FAQ for # the possible risks in this before using chroot_local_user or # chroot_list_enable below. chroot_local_user=YES # # You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their home # directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list of # users to NOT chroot(). # (Warning! chroot'ing can be very dangerous. If using chroot, make sure that # the user does not have write access to the top level directory within the # chroot) #chroot_local_user=YES #chroot_list_enable=YES # (default follows) #chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list # # You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled by # default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on large # sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror" assume # the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for enabling it. #ls_recurse_enable=YES # # Customization # # Some of vsftpd's settings don't fit the filesystem layout by # default. # # This option should be the name of a directory which is empty. Also, the # directory should not be writable by the ftp user. This directory is used # as a secure chroot() jail at times vsftpd does not require filesystem # access. secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty # # This string is the name of the PAM service vsftpd will use. pam_service_name=vsftpd # # This option specifies the location of the RSA certificate to use for SSL # encrypted connections. rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key ssl_enable=NO # # Uncomment this to indicate that vsftpd use a utf8 filesystem. #utf8_filesystem=YES user_sub_token=$USER local_root=/home/$USER/ftp pasv_min_port=10000 pasv_max_port=10100 userlist_enable=YES userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist userlist_deny=NO
Kullanıcıları Ayarlama
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /home/username/ftpsudo chmod a-w /home/username/ftpsudo mkdir /home/username/ftp/uploadsudo chown user:user /home/user/ftp/upload echo "My FTP Server" | sudo tee /home/user/ftp/upload/demo.txt
Yukarıdaki komutlarda gerekli yerleri düzenleyip terminalde tek tek yazmanız gerekmektedir. Şimdi bu komutların ne işe yaradığını tek tek sizlere anlatayım.
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /home/username/ftp bu komut yetisi olmayan /home/username/ftp klasörünün yetkisini belirliyor. (burada username kısmına kullanıcı hesabının username ini yazmanız gerekmektedir.)
sudo chmod a-w /home/username/ftp ile klasörün yetkilerini vermiş olduk.
sudo mkdir /home/username/ftp/upload ile ftp klasörü içinde upload adında bir klasör oluşturduk.
4. satırdaki kodumuz ile bir txt dosyası oluşturduk ve içine My FTP Server yazdık.
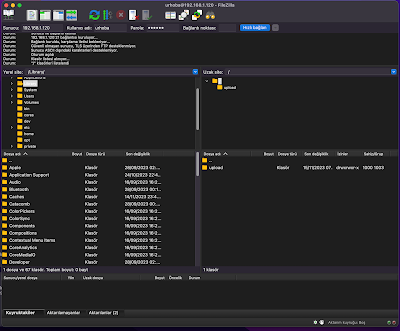
Evet arkadaşlar artık FileZilla ya da herhangi bir FTP bağlantı aracı ile ftp sunucunuza bağlanabilirsiniz.
Not: Buradaki anlatımda herhangi bir SSL ve TLS serfitikası kurulumu yapılmamıştır.



Yorum Gönder